Home | Research | Members | Publications
Current Research | Recent Research | Previous Research
|
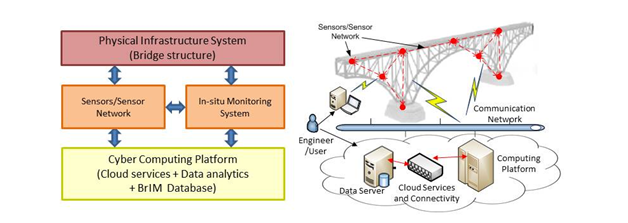
Lifecycle Monitoring of Smart Infrastructures
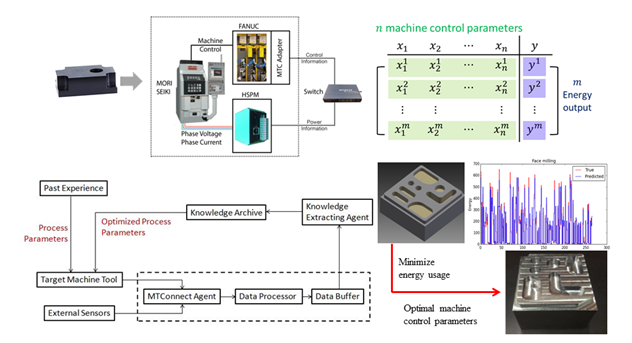
Data Analytics for Smart Manufacturing Systems
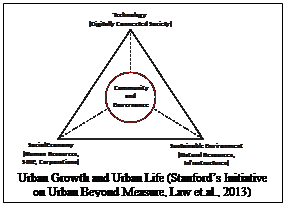
Smart Cities and Smart Communities
Advances in information systems, sensing devices, communication networks, mobile technologies have been and
will continue transforming our societies.
Technology is being used for personal and social reasons.
We have seen a sea change in the use of technology in everyday life and in people attitudes towards digital
commerce and governance in many of the fast growing cities.
Driven by technologies and potential economic benefits, civic leaders, technologists and companies are embracing
and investing to build “Smart Cities.”
The rapid deployment of new technology in many urban cities has changed the landscape on how people interact
and communicate.
A digitally connected world not only changes the business environment, contributing to the social disruptions of
the economy, but also plays a big role in shaping communities and urban life.
But, what constitutes a city or a community to be “smart?”
|
|
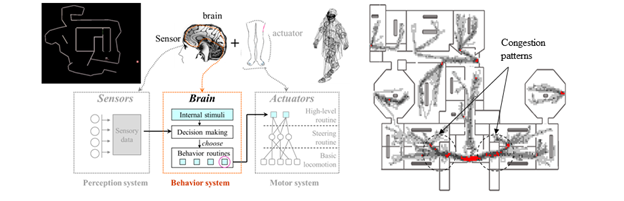
Incorporating Human and Social Behavior in Computational Egress Simulations
The objective of this research is to incorporate the human and social behaviors into a multi-agent based
simulation framework for egress analysis. Studies of past disastrous accidents have shown that human behavior
plays a crucial role affecting evacuation time and patterns.
Decision to evacuate depends on many human factors, such as presence of authorities and individual’s experience
and familiarity with the environment.
Such factors have significant influences, for example, resulting in delayed reaction to initial evacuation.
Crowd density and group relationships can greatly affect evacuation patterns.
Based on analyses of recent fire and emergency events, social scientists have developed theories that attempt to
capture human behavior based on individual characteristics, group relationships and crowd behaviors.
Our current research formalizes and incorporates some of these theories in a multi-agent based computational
framework that will potentially lead to more accurate virtual simulation of emergency evacuation and to better
support “what-if” design scenarios for emergency planning and management.
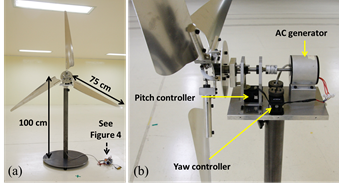
Machine Learning for Wind Farm Power Maximization
The objective of this research is to develop a data driven approach for maximizing energy production in a wind
farm. It is widely recognized that renewable energy can have significant
impact to climate change by reducing the use of fossil fuel. Among various
renewable energy sources, wind power has proven effective for large scale energy production.
For large scale wind farms, wake interference effects are known to affect the power production efficiency of the
wind turbines. This work focuses on a novel approach directly utilizing
data about wind conditions and power production measured from the wind turbines at the site to derive optimal
wind farm control policy. Data-driven optimization schemes have been
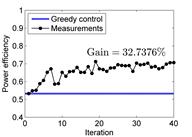
developed to derive the coordinated control actions for wind turbines that maximize the wind farm power production
of the wind farm. Wind tunnel tests on a scaled wind farm model have been conducted to assess the performance of
the control optimization strategy. The result of this study can lead to significant energy production and economic
benefits, while gaining better understanding about the complex wake interference phenomenon in a wind farm.
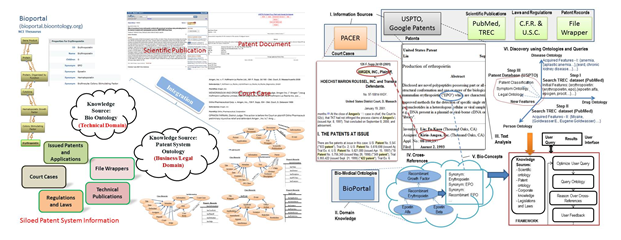
Using Ontologies for Heterogeneous Information Integration – Application to Laws, Regulations and Policies
The goal of this research is to develop a conceptual framework for integrating multiple heterogeneous information
sources using ontologies. The information integration and interoperability
approach takes advantage of ontologies to capture the domaincontext of the information, to reduce the search space
for information access and retrieval, to reason about the information and to, possibly, infer new knowledge which
may not be obvious from the information themselves. Prior research has
dealt with a broad spectrum of application areas in facility engineering, manufacturing system and enterprise
workflow and supply chain integration. Current research focus deals with
management of government regulations and related information (such as guidance documents, court proceedings) and
compliance assistance. Current work includes developing a
patent system ontology to facilitate retrieval of patents and patent related information (such as scientific
literatures, patent file wrappers, and other relevant information). |
|||||||||||
|
Interoperability and Supply Chain
This project is to develop a formal semantic methodology that allows meaningful data exchange across disciplines
and a web services framework that supports integration and collaboration among distributed supply chain
partners.
Flow-based Infrastructure for Composing Autonomous Services (FICAS)
This project is to develop a distributed data-flow infrastructure for composing software services into megaservices.
Management Identifying the Needs of Ocean Ecosystems (MINOE)
This project is to build an ecosystem-based management (EBM) software program for assisting interested parties
navigate through existing laws and regulations.
An Information Management Infrastructure for Patent Laws
This project is to develop a legal informatics system that facilitates searching, retrieval, and relating of
patent laws from distributed sources.
System, Structural and Semantic level interoperability amongst multiple information sources in the patent system
through the use of several ontologies
The bioRegnet project presents an Information Retreival framework across multiple heterogeneous domains.
A Computational Framework for Egress Analysis with Realistic Human Behaviors
This project is to develop a theoretical and computational framework to implement social theories for egress simulation.
Getting to Net-Zero Consumption
This project aims to develop a framework to aid in the design of net-zero buildings.
REGNET: A Distributed Information Management Framework for Environmental Laws
This project, in collaboration with researchers in computer science and law school, investigates the development
of an information management framework for environmental regulations.
REGBASE: A Distributed Information Infrastructure for Regulation Management and Compliance Checking
This project, in collaboration with researcher in computer science, investigates the development of an information
management framework for ADA regulations and guidelines. In addition, simulation and performance analysis for
disabled access, utilizing motion planning techniques, are investigated.
Computational Modeling of Nonadaptive Crowd Behaviors for Egress Analysis
This project investigates human and social behaviors during emergency evacuation. A multi-agent based
computational framework is being designed to simulate crowd dynamics.
Data and Metadata Efforts for the NSF Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulations (NEES)
This project develops a reference data model and tools (for facilitate report generation) for earthquake
engineering experimentations and simulations.
Building Design Services in a Distributed Object Environment
This project attempts to investigate the benefits of the emerging fast speed internet (Internet2) and its impact
in distributed network simulation.
Process Specification and Simulation Access Languages
This project investigates the use of PSL (Process Specification Language) as an exchange standard for process
specification and SIMQL (Simulation Query Language) for the simulation of workflow processes.
Internet-Enabled Simulation of Earthquake Liquefaction Response on Parallel Computers
This project, in collaboration with researchers at University of California, San Diego, aims to develop a finite
element program for simulating earthquake liquefaction response. The simulation program will be run on
state-of-the-art high performance computers and accessible via the Internet.
Internet-Enabled Framework for Collaborative Development of Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis Program
This project, in collaboration with researchers at University of California at Berkeley, is to develop an
internet-based collaborative framework for the development of structural analysis program. The framework is
designed to support collaborative software development by researchers at PEER, a consortium of over 10
universities in the west coast.
A Wireless Modular Health Monitoring System for Civil Infrastructure
This project, in collaboration with researchers at mechanical and electrical engineering, is to develop a wireless
micro-machined electrical mechanical device for vibration testing and structural health monitoring applications.
Active Mediation Technology for Autonomous Engineering Web Services
This project develops an infrastructure for the composition of distributed, autonomous engineering web services.
Internet Business and Intelligent Infrastructure
This project focuses on business strategies for engineering internet commerce and wireless and internet-based
technology and infrastructure to support engineering applications. |
Questions/Suggestions?
Engineering Informatics Group, Y2E2
Building
Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305